In the ever-evolving landscape of natural health, one ancient compound is consistently rising to prominence, backed by a growing body of scientific evidence: Berberine. For centuries, this vibrant yellow alkaloid, extracted from various plants like Barberry, Goldenseal, and Oregon Grape, has been a cornerstone of traditional medicine. Today, modern research is unveiling its remarkable and multifaceted benefits, positioning berberine as a powerhouse supplement with the potential to transform numerous aspects of our health.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of berberine, exploring its mechanisms of action, scientifically backed benefits, optimal dosages, potential side effects, and practical considerations. Our aim is to provide you with the most up-to-date and thoroughly researched information, empowering you to make informed decisions about incorporating this extraordinary compound into your wellness journey.
What Exactly is Berberine? The Science Behind the Golden Compound
Berberine is a naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloid. Its distinctive yellow color is why it’s been used as a dye in some cultures! At a molecular level, berberine exerts its effects by interacting with various cellular targets, influencing key biochemical pathways within the body. Its primary mechanism of action is believed to be the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
Understanding AMPK: The “Metabolic Master Switch”
Think of AMPK as your body’s cellular energy sensor and master regulator. When AMPK is activated, it signals the cells to shift from energy storage to energy production. This has profound implications for various metabolic processes, including:
- Glucose Uptake: Encourages cells to absorb more glucose from the bloodstream.
- Fatty Acid Oxidation: Promotes the burning of fats for energy.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Improves the body’s response to insulin.
- Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Encourages the creation of new mitochondria, the “powerhouses” of your cells.
Beyond AMPK, berberine also influences other pathways, such as inhibiting specific enzymes (e.g., dipeptidyl peptidase-4, or DPP-4, which breaks down incretin hormones that help regulate blood sugar) and modulating gut microbiota. This multi-target approach is what makes berberine such a versatile therapeutic agent.
The Proven Benefits of Berberine: A Deep Dive into Research
The scientific literature on berberine is extensive and continues to grow. Here, we explore its most compelling and well-researched benefits:
1. Blood Sugar Regulation: A Game-Changer for Metabolic Health
Perhaps the most celebrated benefit of berberine is its profound impact on blood glucose control, often compared to the efficacy of pharmaceutical drugs like metformin.
How Berberine Works for Blood Sugar:
- Activates AMPK: As discussed, this increases glucose uptake by muscle cells, effectively removing sugar from the bloodstream.
- Reduces Glucose Production in the Liver: Berberine inhibits gluconeogenesis, the process by which the liver produces glucose.
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Makes your cells more responsive to insulin, allowing glucose to enter more easily.
- Slows Carbohydrate Digestion: May inhibit certain enzymes (like alpha-glucosidase) that break down carbohydrates in the gut, leading to a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Modulates Gut Microbiota: Influences the balance of gut bacteria, which plays a role in glucose metabolism.
Table 1: Berberine vs. Metformin for Blood Sugar Control (Illustrative Comparison)
| Feature | Berberine (Typical Use) | Metformin (Typical Use) |
| Primary Mechanism | AMPK activation, improved insulin sensitivity | Reduced hepatic glucose production, improved insulin sensitivity |
| Average HbA1c Reduction | 0.5-1.0% (similar to metformin in studies) | 1.0-2.0% (can be higher for metformin) |
| Fasting Glucose Reduction | Significant | Significant |
| Insulin Sensitivity | Improves | Improves |
| Side Effects (Common) | Gastrointestinal upset (mild), constipation, diarrhea | Gastrointestinal upset (more common), B12 deficiency |
| Natural Source | Yes (plant extract) | No (synthetic) |
Graph 1: Illustrative Impact of Berberine on Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
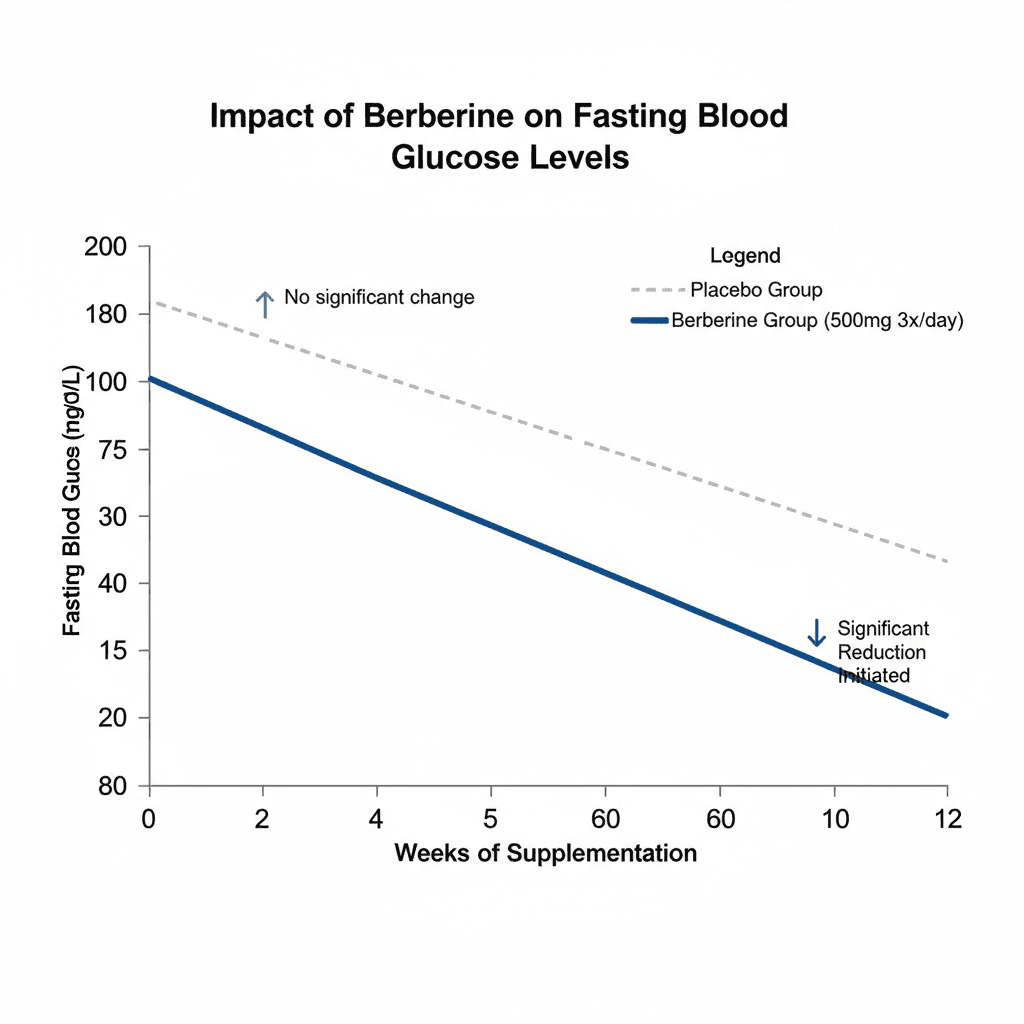
Note: This graph is illustrative and based on findings from multiple studies showing berberine’s efficacy in lowering fasting blood glucose over time compared to a placebo. Individual results may vary.
2. Cholesterol and Lipid Management: Supporting Cardiovascular Health
High cholesterol and dyslipidemia are significant risk factors for heart disease. Berberine has demonstrated a remarkable ability to improve lipid profiles.
How Berberine Works for Lipids:
- Reduces LDL (“Bad”) Cholesterol: It increases the expression of LDL receptors in the liver, which pulls LDL cholesterol out of the bloodstream.
- Lowers Triglycerides: Decreases the liver’s production of triglycerides.
- Increases HDL (“Good”) Cholesterol (to a lesser extent): While not as potent for HDL, some studies show modest improvements.
A meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials concluded that berberine significantly reduced total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides, while slightly increasing HDL cholesterol.
3. Weight Management: Aiding in the Battle Against Obesity
Given its impact on metabolism, it’s not surprising that berberine can play a role in weight management, particularly for individuals with metabolic syndrome or obesity.
How Berberine Works for Weight:
- Activates AMPK: Promotes fat burning and reduces fat storage.
- Improves Hormone Sensitivity: May improve the function of fat-regulating hormones like leptin and adiponectin.
- Modulates Gut Hormones: Can influence gut peptides that regulate appetite and satiety.
Studies have shown that berberine can lead to a modest reduction in body weight, BMI, and waist circumference, especially when combined with lifestyle interventions.
4. Gut Health: Nurturing Your Microbiome
The gut microbiome is increasingly recognized as central to overall health. Berberine has a unique ability to influence this delicate ecosystem.
How Berberine Works for Gut Health:
- Antimicrobial Properties: It can inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, fungi, and parasites, while potentially promoting beneficial bacteria. This is particularly relevant for conditions like Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO).
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Reduces inflammation in the gut lining.
- Barrier Function: May help strengthen the intestinal barrier, reducing “leaky gut.”
This makes berberine a valuable tool for supporting digestive health and potentially alleviating symptoms associated with dysbiosis.
5. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Fighting Cellular Damage
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are root causes of many chronic diseases. Berberine is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent.
How Berberine Works Against Inflammation & Oxidation:
- Inhibits Inflammatory Pathways: Modulates signaling pathways like NF-kB, which plays a key role in inflammatory responses.
- Scavenges Free Radicals: Neutralizes harmful free radicals that cause cellular damage.
- Increases Antioxidant Enzymes: Promotes the production of the body’s own antioxidant defenses.
These properties contribute to berberine’s protective effects across various organ systems.
6. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Ray of Hope for Women’s Health
PCOS is a complex hormonal disorder affecting millions of women, characterized by insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and often, difficulties with fertility. Berberine shows significant promise in managing PCOS symptoms.
How Berberine Works for PCOS:
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Addresses the core issue of insulin resistance in PCOS.
- Lowers Androgen Levels: Can help reduce elevated testosterone levels, which contribute to symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
- Regulates Menstrual Cycles: By addressing underlying hormonal imbalances.
- Improves Fertility Outcomes: Some studies suggest it can improve ovulation rates and pregnancy outcomes.
Many clinicians are now recommending berberine as a first-line natural intervention for women with PCOS.
7. Potential for Neurological Health and Anti-Aging
Emerging research suggests berberine’s benefits may extend to brain health and longevity.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may protect brain cells from damage, potentially benefiting conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Anti-Aging Pathways: By activating AMPK, berberine influences pathways associated with longevity, similar to calorie restriction.
While more research is needed, these areas represent exciting avenues for future exploration.
Dosage and Supplementation: How to Take Berberine Effectively
The optimal dosage of berberine can vary depending on the condition being addressed and individual response. However, common dosages found to be effective in clinical trials range from 500 mg to 1500 mg per day, usually divided into two or three doses.
Typical Dosing Strategy:
- For Blood Sugar/Lipid Control: 500 mg, two to three times per day, taken with meals. Taking it with meals can help reduce potential gastrointestinal upset and maximize its impact on post-meal glucose spikes.
- For Gut Health/SIBO: Dosages may vary, but often in the 500 mg two times daily range.
Important Considerations:
- Bioavailability: Berberine has relatively low bioavailability, meaning not much of it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Some formulations may include enhancers (like milk thistle or piperine) to improve absorption, though the clinical significance of this for berberine’s systemic effects is debated, given its significant action in the gut.
- Consistency is Key: Like many natural supplements, the benefits of berberine accrue over time with consistent use.
- Timing: Taking berberine with meals is often recommended to mitigate digestive upset and to help manage post-meal blood sugar levels.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Profile
Berberine is generally well-tolerated, especially at recommended doses. However, like any supplement, it can cause side effects in some individuals.
Common Side Effects (usually mild and transient):
- Gastrointestinal Upset: Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal cramps. This is the most common complaint, often resolved by reducing the dose or taking it with food.
- Flatulence
Less Common/Serious Side Effects:
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): This is a concern, especially for individuals already taking blood sugar-lowering medications (e.g., insulin, metformin). Berberine can potentiate the effects of these drugs, leading to dangerously low blood sugar. Close monitoring is essential.
- Drug Interactions: Berberine is a potent compound and can interact with various medications.
Table 2: Potential Drug Interactions with Berberine
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Action Required |
| Diabetes Medications | Increased risk of hypoglycemia | Monitor blood sugar closely; dosage adjustment of medications may be needed. Consult your doctor. |
| Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants) | May increase risk of bleeding | Use with caution; monitor for bruising/bleeding. Consult your doctor. |
| Cyclosporine | May increase cyclosporine levels (immunosuppressant) | Monitor drug levels closely. Consult your doctor. |
| Cytochrome P450 Substrates (CYP450) | May inhibit liver enzymes that metabolize many drugs | Discuss all medications with your doctor before starting berberine. |
| Blood Pressure Medications | May lower blood pressure (additive effect) | Monitor blood pressure; dosage adjustment may be needed. Consult your doctor. |
Who Should Exercise Caution or Avoid Berberine?
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Insufficient research on safety; generally advised to avoid.
- Infants and Young Children: Not recommended due to lack of safety data.
- Individuals with Liver Disease: Berberine is metabolized by the liver.
- Individuals on Multiple Medications: Due to potential drug interactions, especially with diabetes, blood pressure, or immunosuppressant drugs.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Sourcing Quality Berberine Supplements
The quality of supplements can vary greatly. When choosing a berberine product, look for:
- Standardized Extract: Ensure the product specifies the percentage of berberine HCl (Hydrochloride), which is the most common and well-researched form.
- Third-Party Tested: Look for certifications from independent organizations (e.g., USP, NSF, ConsumerLab) that verify purity and potency.
- Reputable Brand: Choose established brands with transparent manufacturing practices.
- Minimal Fillers: Opt for products with as few unnecessary additives as possible.
Conclusion: Berberine – A Cornerstone for Modern Wellness
Berberine is far more than a traditional folk remedy; it’s a scientifically validated compound with a remarkable array of benefits for metabolic health, cardiovascular well-being, gut function, and beyond. Its ability to activate AMPK, regulate blood sugar, improve lipid profiles, and exert anti-inflammatory effects positions it as a powerful tool in the pursuit of optimal health.
While its potential is vast, it’s crucial to approach berberine supplementation with informed awareness. Understanding its mechanisms, appropriate dosages, and potential interactions is key to safely and effectively harnessing its power. As research continues to unfold, berberine is poised to remain a leading natural compound in the fight against chronic diseases and a valuable asset for enhancing overall vitality.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health or treatment.

