Moringa oleifera, often called the “miracle tree,” is a plant packed with nutrients like iron, vitamins, and proteins. It’s commonly used in places like Asia and Africa to help with health issues during pregnancy and breastfeeding. A recent review study examined research from 2018 to 2023 to investigate the benefits of Moringa in addressing anemia (low blood iron) and other health-related issues, including maternal health, infant growth, and milk production. This article explains the findings in easy words, using tables and graphs to make it clear. No fancy terms—just simple facts to help you understand.
What is Moringa and Why Use It?
Moringa is a tree that grows easily in hot, dry places. Its leaves are full of good stuff like iron, calcium, and vitamins A, B, C, and E. During pregnancy, moms need extra nutrients because their body changes a lot. Breastfeeding moms need them too for making milk. The study reviewed 12 papers, mostly from Indonesia, showing Moringa can help without side effects. But always talk to a doctor before trying it!
How Moringa Helps with Anemia in Pregnancy
Anemia is when you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells, often from low iron. It’s common in pregnant women, especially in poor countries. Moringa has lots of iron, so it can help boost blood levels.
Table 1: Key Studies on Moringa and Anemia
This table shows some main studies, what they did, and what happened.
| Study Location | Design | What They Gave | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Sulawesi, Indonesia | Compared groups | 4 capsules/day of Moringa leaf powder (500 mg each) vs. iron-folic acid (IFA) | Higher hemoglobin (blood health), less stress, higher baby birth weight. |
| Gorontalo, Indonesia | 6-week treatment | Moringa extract vs. IFA | 54% had 0.1-1.0 g/dL hemoglobin increase; better than IFA (only 22%). |
| Makassar, Indonesia | 3-month trial | Moringa leaf extract (800 mg x2/day) vs. IFA | Improved arm size (nutrition sign), but less weight gain than IFA. |
| Other Indonesia studies | 60-day trials | Moringa biscuits (2/day with 2.8g Moringa) + iron vs. iron alone | Better blood values like MCH, MCHC, MCV; no big hemoglobin change. |
From these, Moringa works as well as or better than regular iron pills for blood health.
Graph 1: Hemoglobin Increase from Moringa
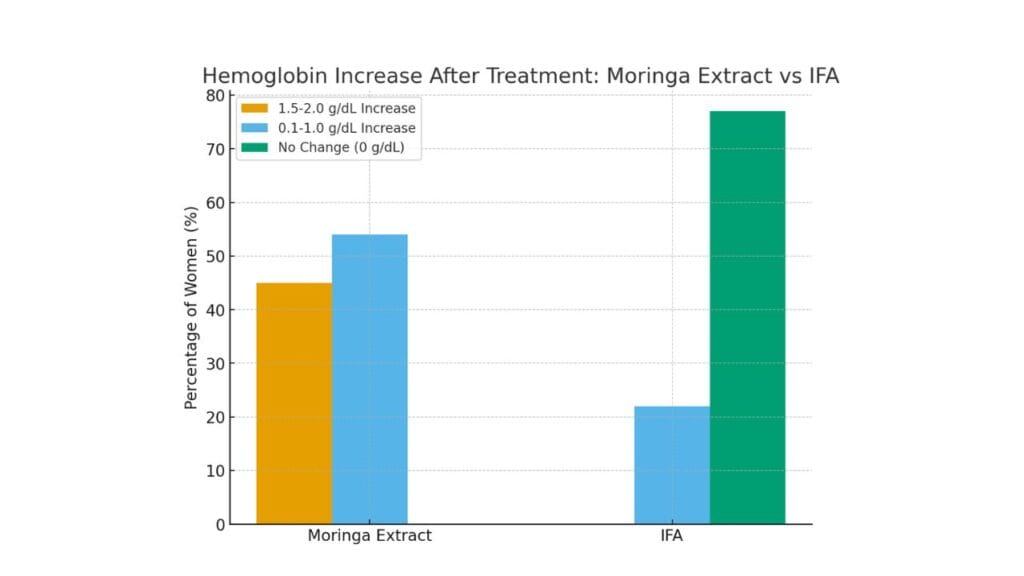
Here’s a side-by-side comparison chart of hemoglobin increase in women after treatment:
- Moringa extract:
- 45% had a 1.5–2.0 g/dL increase
- 54% had a 0.1–1.0 g/dL increase
- None showed no change
- IFA (Iron-Folic Acid):
- 22% had a 0.1–1.0 g/dL increase
- 77% showed no change
👉 This makes it clear that Moringa extract was far more effective than IFA.
Moringa for Mom’s Health and Milk Production
Moringa isn’t just for anemia. It can help moms feel better and make more milk. It has stuff like flavonoids that boost hormones for milk.
- Mom’s Nutrition: In one study, Moringa helped with weight and arm size, but moms still needed more vitamins from food.
- Milk Boost: As a “galactagogue,” it increases milk. Biscuits with Moringa given right after birth helped babies gain weight faster by day 7.
- Milk Quality: One study saw stable healthy fats (like DHA for baby’s brain) in milk from moms taking Moringa extract.
Table 2: Effects on Breastfeeding and Milk
| What They Studied | How Moringa Was Given | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Milk production | Biscuits post-delivery + iron/vitamin A | Babies gained more weight by day 7; better milk flow. |
| Milk fats (DHA/AA) | Leaf extract or powder for 30 days | Stable DHA levels; no big differences vs. IFA. |
| Long-term milk effect | Capsules for 3 months | Better baby growth in some measures, like preventing short height. |
How Moringa Helps Babies
Babies benefit too! Moms taking Moringa had healthier kids.
- Birth Weight: Higher in Moringa groups.
- Growth: Less stunted growth (short for age) in kids up to 42 months.
- Development: 91.5% normal social skills in kids of moms on Moringa powder.
- Health: Fewer sick days in first 6 months; Moringa was way better than iron pills.
Graph 2: Child Development Outcomes
A pie chart to show how kids developed.
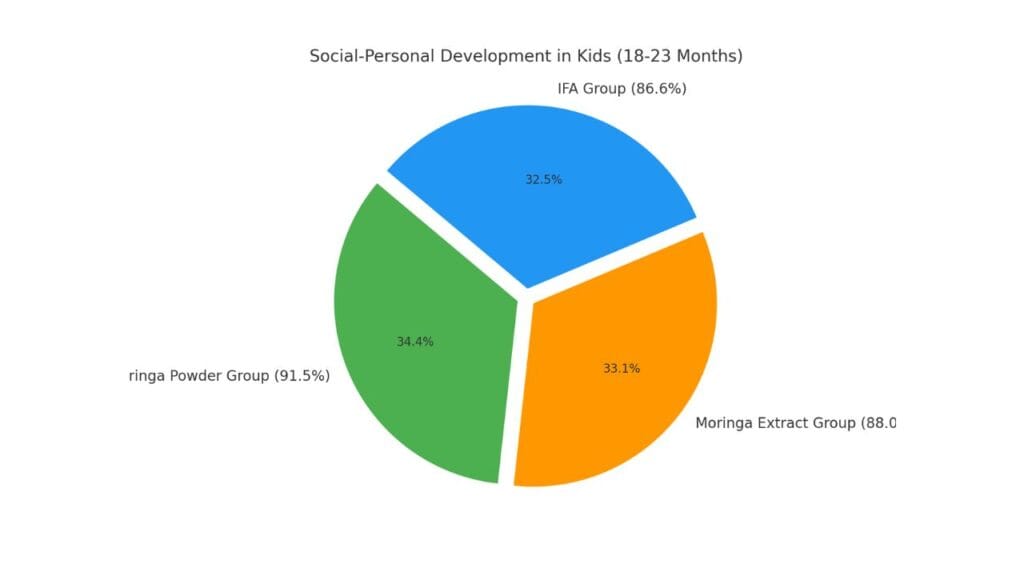
Here’s the pie chart showing Social-Personal Development in Kids (18–23 Months) across different groups:
- Moringa Powder Group: 91.5%
- Moringa Extract Group: 88.0%
- IFA Group: 86.6%
👉 The chart shows that Moringa Powder had the best outcomes for social-personal development in children compared to the other groups.
Limitations and Tips
The studies were mostly in Indonesia, so results might differ elsewhere. Doses and forms (powder, extract, biscuits) varied, so no exact “how much” guide. No bad side effects found, but more research needed.
Tips for Using Moringa Safely:
- Start with small amounts, like 500-800 mg/day powder or extract.
- Mix in food like biscuits or tea.
- Combine with doctor’s advice and balanced diet.
- Good for low-income areas where Moringa grows easily.
Table 3: Simple Tips Table
| Tip | Why It Helps | How to Do It |
|---|---|---|
| Limit to recommended dose | Avoid too much | 2-4 capsules/day, check with doctor. |
| Use during pregnancy | Fight anemia | Add to meals for iron boost. |
| For breastfeeding | More milk | Eat Moringa biscuits or leaves. |
| Monitor baby health | Track benefits | Weigh baby regularly, note sickness. |
Wrapping Up
Moringa seems like a safe, natural helper for pregnancy and breastfeeding, especially for anemia, milk, and baby growth. It’s cheap and grows easily in many places. But it’s not a magic fix—eat well and see a doctor. For the full study, check.
Read More: The Health Benefits of Moringa Oleifera: A Comprehensive Overview

